Formative assessments are where students are quizzed periodically throughout a learning unit. Unlike traditional assessments, these insights provide you with regular and reliable feedback on student progress. Whether it’s polls, discussions, debates or reflections, frequent, low-stakes assessments let students apply what they have learned thus far. At a time when students place increased value on frequent feedback from their educators, facilitating regular assessments is essential. Below, we share:
- What formative assessments are
- What the differences are between formative and summative assessments
- How to engage students with formative and summative assessments
- The tools you’ll need to run formative assessments
- The benefits of formative assessments
- 20 formative assessment examples for any course or discipline
What are formative assessments?
Formative assessments involve monitoring student progress regularly throughout a course so that educators can better gauge students’ learning gaps and address those early on. Basic formative assessment strategies may include concept maps, responses posted to a discussion board and an ungraded quiz or poll.
Watch the video below to learn how formative assessments in the classroom can benefit both educators and students. You’ll also get assessment ideas that Leslie Sprunger, Associate Dean for Professional Programs in the Faculty of Integrative Physiology and Neuroscience at Washington State University, uses in her own courses.
How to engage students with formative assessments
Well-designed assessments encourage students to prioritize intellectual growth, while equipping them with marketable skills for their future careers. There are three main types of assessments instructors can incorporate into their higher educations courses.
- Assessments as learning opportunities: The best assessments are educational opportunities in which students can practice different methods of synthesizing, analyzing, and communicating what they have learned. There are many ways students can demonstrate mastery of the course content that go beyond traditional papers, quizzes and examinations. Giving students choice in how they express their knowledge, such as unessays, short films, collaborative blogs and field work also enables students to build their personal portfolios and resumes.
- Assessments that are self-reflective: Rather than objective assessments, instructors can create opportunities for students to reflect on their own progress. Consider asking students to students keep a journal throughout the class is a great way to create a record of their semester-long evolution. You can also ask students to evaluate their own work, as well as their peers. This way, instructors empower students to take ownership of the assessment process.
- Assessments that happen over time: One popular method is incorporating “scaffolding” into assessments. Instead of a paper worth a large proportion of the final grade, students submit several smaller assignments throughout the course of writing their paper, each worth a fraction of the overall grade and building towards the final product. For instance, they might first submit a topic and thesis statement, followed by their outline, then a rough draft, and then the final paper. This method provides students with feedback at various points, prioritizes the process of writing, and lowers the stakes for each graded piece of work.
Formative vs. summative assessment: The difference
Formative and summative assessments can easily be confused. Summative assessment remains an essential part of every single college course being offered today. Despite its widespread use, however, an over-reliance upon it can turn the benefits into drawbacks:
- Every summative assessment is a high-pressure situation for students.
- Poor performance on an early assessment only increases the pressure on subsequent assessments. If a student earned a C on the midterm, they’ll feel the need to ace the final just to end up with a B.
- Poor performance on an early assessment undermines students’ confidence in their ability to perform better in the latter stages of the course. This creates an incentive to cheat: if they need to ace the final, they’ll find a way.
The best way to design any summative assessment is to make it an integral part of course planning.
Formative vs summative assessment: A structured approach
While formative assessment can take place informally through classroom discussion, it also benefits from a planned approach to its use. The challenge, for educators, is to strike the right balance between checking in on the progress of student learning and putting that learning to the test.
Choosing between formative and summative assessment for a particular course isn’t an either-or proposition. Formative assessment can’t substitute for traditional summative assessment, since exams and assignments remain essential as the best way to definitively measure student proficiency and assign a grade.
Some faculty who have embraced formative assessment choose to make the final exam worth 100 percent of their students’ grades, conducting formative evaluations throughout the semester to the point where come exam day, they and their students are confident of success. This formula probably wouldn’t work for every professor or every course, but it is a testament to the effectiveness of formative assessment, and to the value of making thoughtful use of both assessment types in every course you teach.
We share the key differences between formative and summative assessments in the table below.
| Formative assessments | Summative assessments |
| Monitor student learning throughout the course | Evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit |
| Are low-stakes or have no point value attached | Are high-stakes and are often cumulative |
| Offer more flexibility in how to assess students (examples of formative assessment may include think-pair-share activities or hands-on learning) | Aren’t as flexible in assessment type (papers or essays are commonly used) |
| Are used to determine where to adjust lessons and remaining instruction | Are used to determine subject master |
Tools you can use to run formative assessments
Depending on what type of assessment you’re looking to run—whether a quiz or group discussion—the technology required will vary. Different disciplines, such as STEM or Humanities courses, may also require different formative assessment tools in order to run simulations or lab activities.
That said, plenty of the 20 formative assessment strategies we share later in this post can also be facilitated with pen and paper or simple tech tools. If you’re looking to use ed tech to run your formative assessments, here are some platforms you may want to consider.
- Quizzes: Kahoot!, Quizlet, Socrative, Top Hat
- Video-based assessment: Animoto, Flipgrid, PlayPosit
- Discussions: Backchannel Chat, Discord, Top Hat (with anonymous discussion capabilities)
- Whiteboard or note taking tools: Dotstorming, Padlet, Limnu
- Tools for STEM classes: BeyondLabz, Labster, Top Hat Labs
- Tools for Humanities classes: Annotation Studio, Audacity, Canva, Top Hat
20 formative assessment examples for any course or discipline

Assessing course-related skills and knowledge
These formative assessment examples help evaluate learning of a given subject’s content by assessing student understanding and information recall from previous courses. Assessing this knowledge is especially important for instructors at the beginning of the term, in order to provide a clearer understanding of how to proceed with course material.
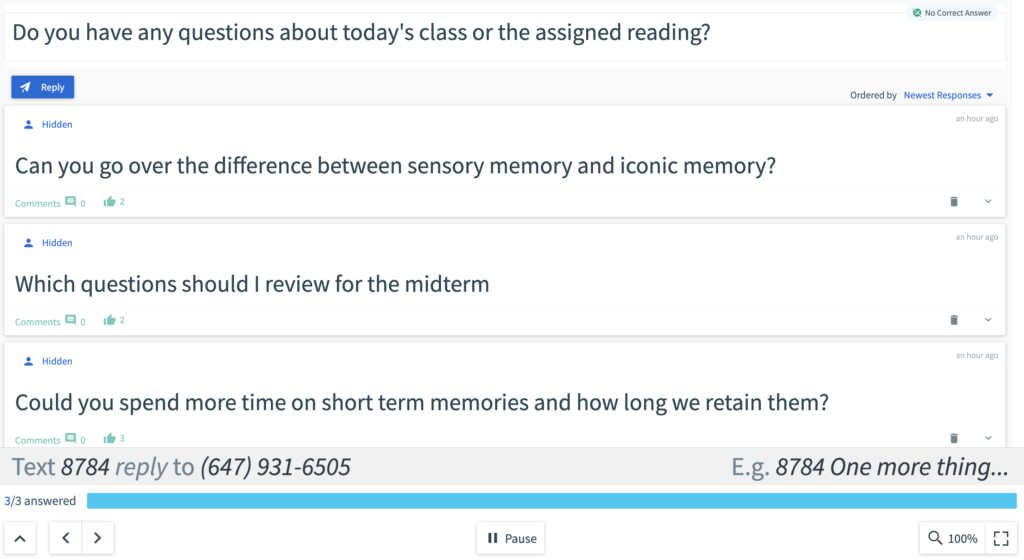
1. Exit tickets/exit slips:
Rather than a formal assessment, students use exit tickets to answer one or more assessment questions at the end of a class period or online course module to demonstrate how well they’ve absorbed that particular lesson. Each question should focus on a single concept or skill taught in that lesson. Download your free exit ticket formative assessment template for your next course.
2. One-minute paper:
In this informal assessment example, students are prompted to write a short response answering two questions related to a given week’s course content. Responses to one-minute papers can also be posted in online discussion forums to spur conversation between students. Questions can be as simple as: What was the most valuable, important or useful thing you learned in the lesson? What key questions, problems or issues remain unresolved?
Are you looking to further assess students in and out of your classroom? Top Hat’s formative assessment capabilities can help. Facilitate the one-minute paper exercise in-app using an interactive discussion board. Platforms like Kahoot! and Socrative can also be used for running polls and discussions as a quick formative assessment example.
Developing critical thinking and analysis skills
Consider structuring formative assessment examples around the development of higher-order thinking skills that rely on metacognition. Various modes of analysis, including the ability to break down information, problems and questions help develop students’ critical thinking skills. Students who think critically become instinctual problem solvers in class, engineering creative solutions to solve complex real-world case studies.
3. Think-pair-share:
Students work together in pairs or small groups to answer a question or solve a problem related to an assigned reading. These groups can use dedicated chat channels built into active learning platforms to communicate and discuss their ideas. First, the instructor asks an assessment question regarding the text for students to think about. Next, students pair up with one or more fellow students to discuss the question and their thoughts on the possible answers. Finally, each pair or group shares their conclusions with the rest of the class.
4. Defining features matrix:
Students categorize concepts based on whether or not they contain certain defining features. This is particularly useful for assessing how fully students understand certain factors distinguishing various concepts from one another and how well they can analyze whether a particular concept fits a certain category.
5. Socratic seminar:
Students help one another apply the ideas, issues and values reflected in a course text through a group discussion. Ask students to annotate the text in advance of class in order to familiarize themselves with the key themes and ideas discussed. Pose a general question and encourage students to share their responses with the group. Another student then responds to the last thought that was shared.
Encouraging students to think creatively

Quick formative assessments can involve creative expression. The following examples of formative assessments are used to understand student abilities when synthesizing information. By instructing students to express themselves creatively, students have the opportunity to think outside the box.
6. Word journal:
This assessment is conducted in two parts. In the first part, the student summarizes an entire lesson in a single word. In the second part, the student composes a short statement of one or two paragraphs explaining why they chose that particular word to summarize the lesson. These can then be submitted to the instructor for feedback directly through content delivery platforms or your learning management system (LMS).
7. Invented dialogue:
This strategy is particularly useful for demonstrating how well students have synthesized various historical or literary personalities, settings or themes. In this assessment, students compose a fictional dialogue between two real or fictitious personalities that demonstrate the students’ understanding of the topic. Teachers can opt to instruct students to incorporate actual quotes from primary sources into the dialogue or to simply invent plausible quotes of their own based on their comprehension of the content.
Enhancing problem-solving skills
These formative assessment examples assess students’ problem-solving abilities, including their ability to recognize the various types of problems and any causes and appropriate techniques to solve them. Learners can also use the time to draw similarities between various features of different problems, reflect upon them and adjust strategies for solving them accordingly. They are an important component for every educator to have on their formative assessment checklist.
8. Documented problem solutions:
Similar to a show-and-tell exercise or a how-to article, students write down each step they went through in solving a particular problem. This helps instructors understand how a student goes about thinking through problems and may highlight student obstacles when efficiently solving different types of problems. A variation of this is to document the student’s problem-solving process through an audio-video recording of the student demonstrating their process.
9. Problem-and-solution type recognition:
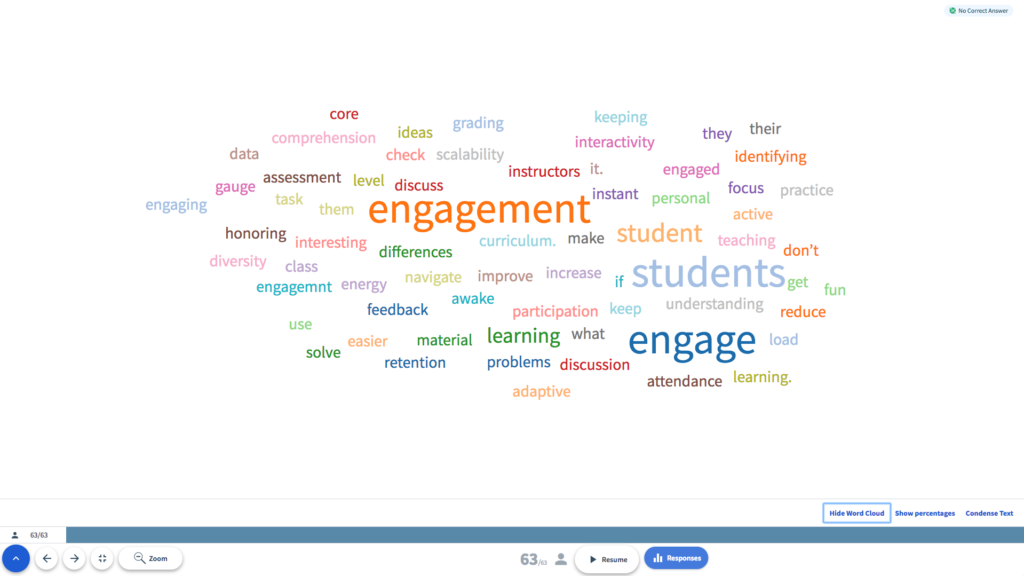
Effectively solving any problem requires the ability to identify the type of problem and, subsequently, the most appropriate methods of solving it. Students are given a problem and must identify its type, such as routine or non-routine, well-defined or ill-defined, and the most likely type of solution to apply to it, such as algorithm, heuristics or trial and error. Students can answer these problems through a short-answer question and the results can be shown to the class using a word cloud display.
Assessing student performance and application abilities

These formative assessment examples assess students’ understanding of how to apply the knowledge they’ve learned to specific situations. These informal assessment examples can stand alone as “temperature checks” or can be a part of a longer assessment, such as a scheduled test or quiz.
10. Directed paraphrasing:
Students take a lesson and paraphrase it with a particular audience in mind. This not only helps to assess a student’s understanding of the topic, it also helps to assess their ability to reframe it in a way that people in a different context and setting can likewise understand and apply it.
11. Student-generated test questions:
As a form of role-reversal, students devise test questions and sample appropriate answers that demonstrate their ability to comprehend concepts that underlie assigned readings. Rather than simply requiring students to recall what they’ve read, it asks them to hone in on the key elements that would indicate to them another person’s full comprehension of the concepts.
Understanding student self-awareness, attitudes and values
These formative assessment examples engage students and motivate them to develop their own attitudes, values, opinions and self-awareness through course-related activities. The three quick formative assessments below can be used as an exercise to generate discussion amongst students and ensure learning continues once class is over.
12. Opinion polls:
Students indicate how much they agree or disagree with a particular prompt or statement. This assessment data can help educators see how comfortable students are with regard to key objectives of learning activities and with specific course content in particular.
13. Profiles of admirable individuals:
This assessment in the classroom involves asking students to write a brief biography of a real person involved in a relevant field that highlights the admirable characteristics making them a role model. Instructors can use polling features for students to vote on which expert in the field they would like to research.
14. Everyday ethical dilemma: Students answer how they would go about solving a common everyday ethical dilemma related to the course or their discipline.
Activities that help develop individual awareness of self as a learner
These formative assessment examples help students clarify and express their self-concept and personal goals in ways that connect to the course content.
15. Focused autobiographical sketch:
Students write a brief memoir-style essay describing a moment or episode of their lives during the course in which they felt like they successfully reached a learning outcome.
16. Goal-ranking:
Students list three to five goals of their own that serve as their learning goals of the course, then rank them in order of priority. At the end of the course, instructors can go back to this exercise and have students evaluate their rankings and/or assess how well they did achieving each goal they set. Using Top Hat’s heat map question functionality, instructors can show how the class performed as a group.
Understanding student learning behaviors, strategies and skills

These formative assessment examples help instructors assess students’ learning habits. They can help create a more tailored learning experience.
17. Productive study-time log:
Students keep a log of all the time they spent learning and studying for a given course and, alongside each entry, the quality of that time. This acts as a form of self-assessment because it helps both students and educators see how effectively students are making use of their study time.
18. Punctuated lectures:
After listening to a lecture, students reflect (in writing) on how well they were concentrating on the material and, by contrast, how often they became distracted. They may also note how they brought their attention back to the material, if at all, so they can arm themselves with these tools in future lectures. They can even add how the lecture met their expectations and how they connected the lecture to knowledge they already possess. This can be submitted through the class’s live chat while lectures are occurring, so students are able to view their peers’ thoughts and opinions.
Assessing student reactions to learning
These formative assessment examples help instructors assess how well students can identify the key points and learning outcomes of a given lesson. These formative assessment ideas will let students thoughtfully reflect on a given reading or artifact.
19. Feedback forms:
There are several ways to solicit weekly feedback from students after a lesson. Educators can pose a series of questions, or even a single question, about the lesson’s effectiveness. These can be multiple-choice, true/false, yes/no or open-ended questions.
20. RSQC2:
Students compose a brief statement regarding a particular lesson written in the following format: Recall, Summarize, Question, Connect, Comment. This can also take place in a discussion forum, so students can comment on each other’s questions and ideas.
Resources:
Formative and Summative Assessments. (n.d.). Yale Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning. https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/Formative-Summative-Assessments
What is the difference between formative and summative assessment? (n.d.). Eberly Center at Carnegie Mellon University. https://www.cmu.edu/teaching/assessment/basics/formative-summative.html
50 CATS by Angelo and Cross. (n.d.). University of California, San Diego. https://vcsa.ucsd.edu/_files/assessment/resources/50_cats.pdf


